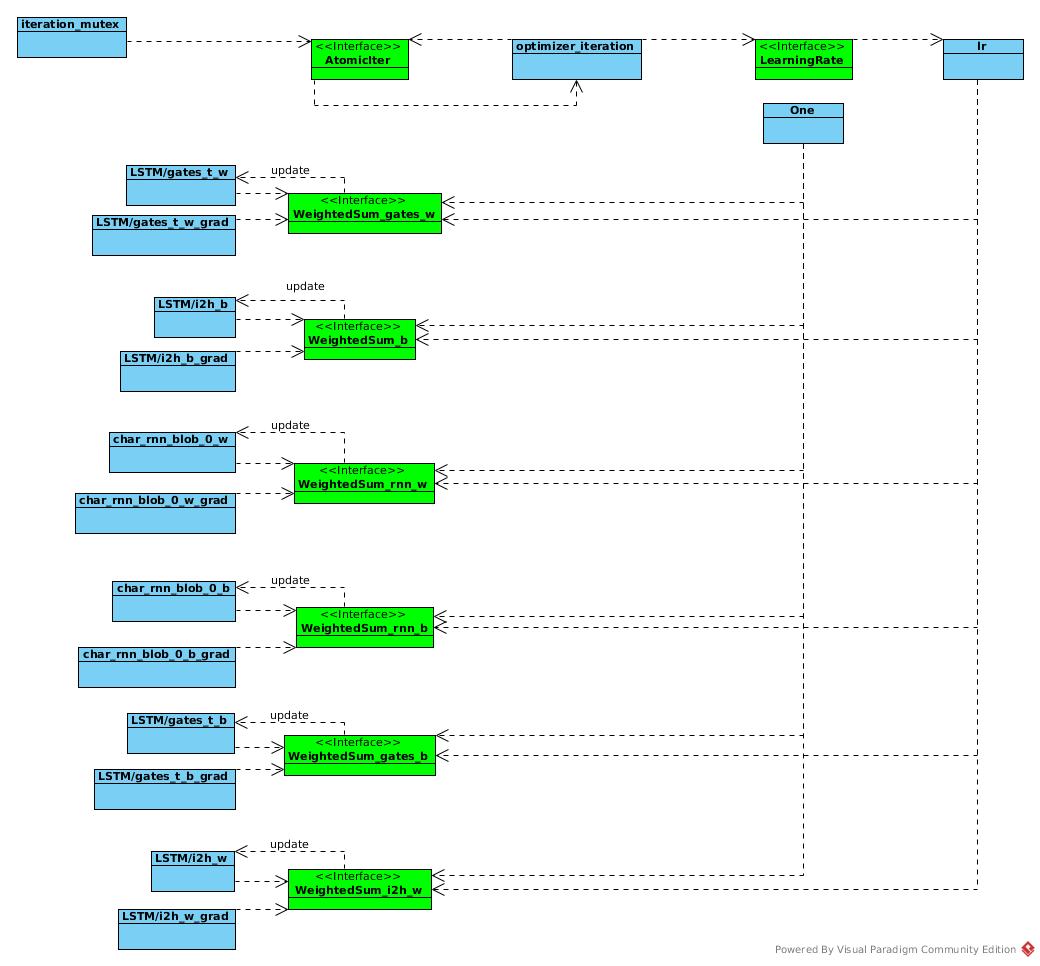
RNN Operation
Codes
Overview
The rnn.cpp defined the 3 models, all models have both run-net and init-net
- training model, named t
- predict model, named model
- data pre processing model, named prepare
The run-net is shared by training model and predict model.
From model-net view, the architecture is like:
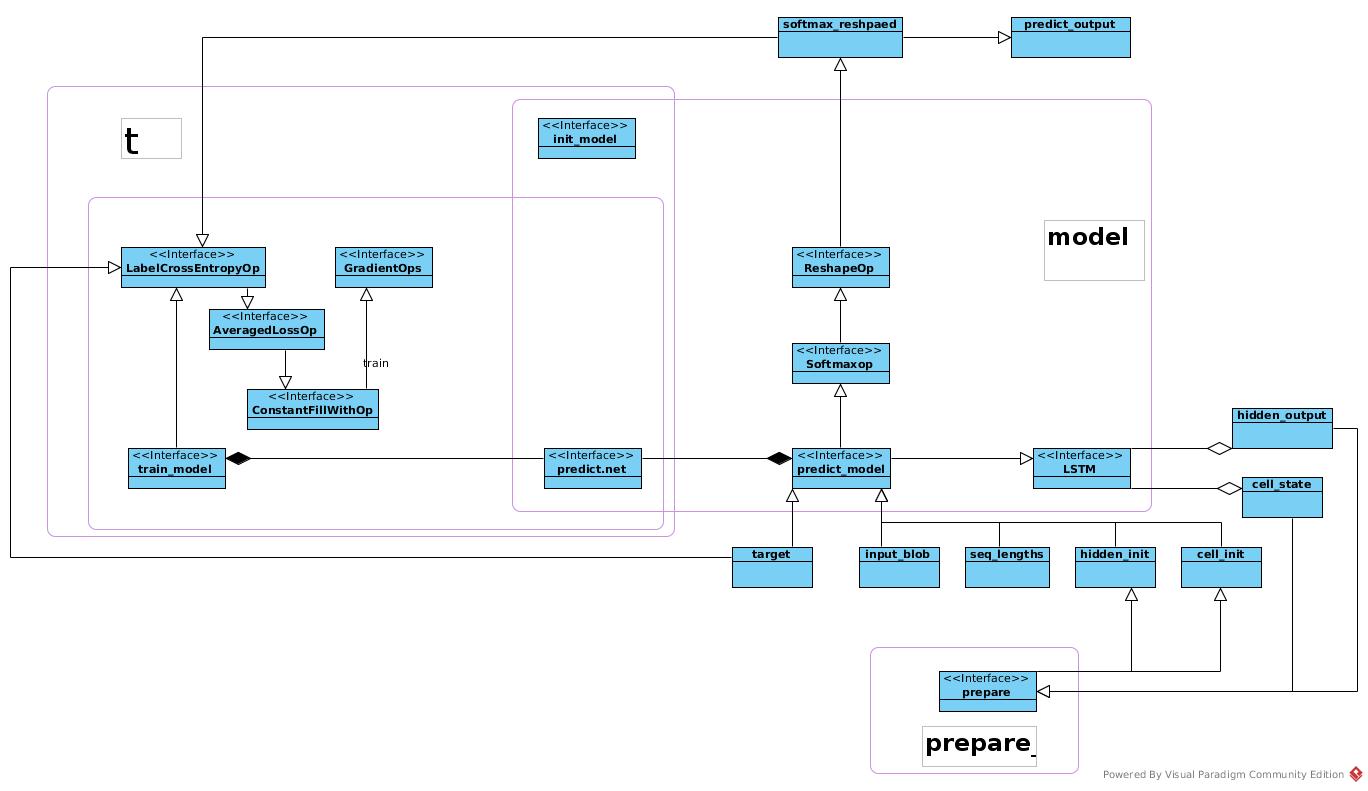
rnn_net
The rnn net is defined as an operator in AddLSTM and AddRecurrentNetworkOp
Overview of the LSTM is like:
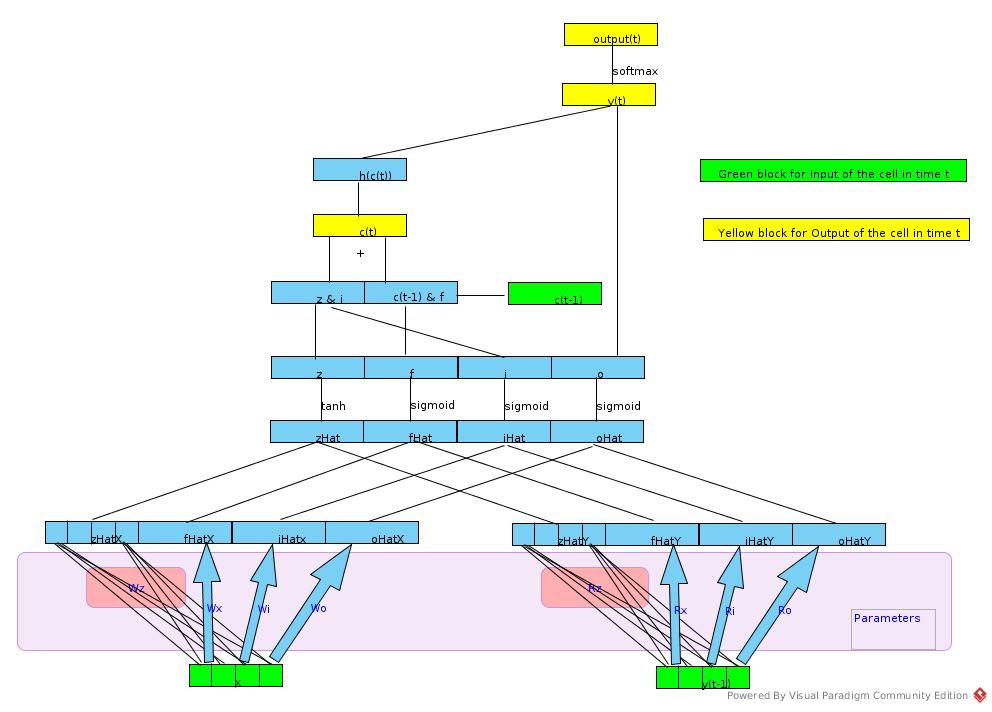
AddLSTM
AddFcOps(input_blob, scope + "/i2h", vocab_size, 4 * hidden_size, 2);
The line of the codes deals with (Wz * x) in above picture. This part has nothing to do with recurrent operations, and the FcOp processes this part from 0 to SeqLen once for all.
*hidden_output = scope + "/hidden_t_last";
*cell_state = scope + "/cell_t_last";
This part defines output of recurrent network.
initModel.AddXavierFillOp({4 * hidden_size, hidden_size},
scope + "/gates_t_w");
trainModel.AddInput(scope + "/gates_t_w");
initModel.AddConstantFillOp({4 * hidden_size}, scope + "/gates_t_b");
trainModel.AddInput(scope + "/gates_t_b");
This part initializes Rz (refer to above figure).
AddRecurrentNetworkOp
Define simple network for step operation in recurrent network
Workspaces
The RNN network is built as an operator and step network is built as an argument, for workspace coherence, the workspace is set by an input argument scope + “/step_workspaces”:
auto op = trainModel.AddOp("RecurrentNetwork",
{scope + "/i2h", hidden_init, cell_init, scope + "/gates_t_w",
scope + "/gates_t_b", seq_lengths},
{scope + "/hidden_t_all", hidden_output, scope + "/cell_t_all",
cell_state, scope + "/step_workspaces"}
);
//recurrent_network_op.h
template <class Context>
class RecurrentNetworkGradientOp final : public Operator<Context> {
public:
USE_OPERATOR_CONTEXT_FUNCTIONS;
RecurrentNetworkGradientOp(const OperatorDef& operator_def, Workspace* ws)
: Operator<Context>(operator_def, ws),
sharedWs_(ws),
The RecurrentNetworkOp and GradientOp assign a collection of workspaces, one for each time step.
//DoRunWithType
const detail::ScratchWorkspaces& scratch =
this->template Input<detail::ScratchWorkspaces>(InputSize() - 1);
const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Workspace>>& stepWorkspaces =
scratch.stepWorkspaces;
CAFFE_ENFORCE_GE(stepWorkspaces.size(), seqLen);
Workspace& sharedBlobsWs = *scratch.sharedBlobsWs.get();
Workspaces are organized as inherent tree, with input workspace argument as sharedBlobsWs shared by all time step workspaces.
//DoRunWithType()
for (auto t = 0; t < seqLen; ++t) {
auto& currentStepWorkspace =
(has_backward_pass ? stepWorkspaces[t] :
stepWorkspaces[t % num_workspaces_on_fwd_only]);
if (!currentStepWorkspace) {
currentStepWorkspace = std::make_shared<Workspace>(sharedBlobsWs.get());
}
The StepNetwork is created in the corresponding workspace:
for (auto t = 0; t < seqLen; ++t) {
//...
if (rnnExecutor_) {
if (!has_backward_pass) {
// Need to limit timestep parallelism because we cycle over workspaces
rnnExecutor_->SetMaxParallelTimesteps(num_workspaces_on_fwd_only);
}
rnnExecutor_->EnsureTimestepInitialized(
t, currentStepWorkspace.get(), this->observers_list_);
} else {
detail::UpdateTimestepBlob(currentStepWorkspace.get(), timestep_, t);
auto* stepNet = currentStepWorkspace->GetNet(stepNetDef_.name());
if (stepNet == nullptr) {
stepNet = currentStepWorkspace->CreateNet(stepNetDef_);
}
}
Why should assign a workspace for each step?
- For RNN, each time step may receive different input and generate temporary output with the same blob names. Different workspaces with same shared workspace encapsulate all temporary blobs in one workspace.
- For some complex networks, the operators in step could be executed in parallel, esp. in GPU cases.
- It is obvious that the RNN operator has been designed in this way
- The LinkOperator has been inserted into StepNetwork in RecurrentNetworkOp, and the LinkOperators would be executed in each step.
- The temporary output of internal operators. In this simple case, the temp blob is LSTM/gates_t ``` c++ //RecurrentNetworkOp links_ = constructLinks(); aliases_ = constructAliases();
stepNetDef_.add_external_input(timestep_); detail::AddApplyLinkOps( links_, timestep_, operator_def.device_option(), &stepNetDef_);
In this simple case, the blobs that encapsulated in local workspace are link internal blobs, including: ``` c++ Local blob LSTM/cell_t Local blob LSTM/cell_t_prev Local blob LSTM/gates_t Local blob LSTM/hidden_t Local blob LSTM/hidden_t_prev Local blob input_t Local blob timestepIn backward steps, the workspaces created in forward steps are transferred as inputs:
struct GetRecurrentNetworkGradient : public GradientMakerBase { using GradientMakerBase::GradientMakerBase; std::vector<OperatorDef> GetGradientDefs() override { //... std::vector<std::string> gradientInputs; //... // All inputs and outputs are passed back for (int i = 0; i < def_.input_size(); ++i) { gradientInputs.push_back(I(i)); } //... return SingleGradientDef( "RecurrentNetworkGradient", "", gradientInputs, gradientOutputs); }And extracted later:
template<typename T> bool DoRunWithType() { //std::cout << "RecurrentNetworkGradientOp" << std::endl; const auto seqLen = Input(gradInputs_.size()).dim32(0); VLOG(1) << "seqLen: " << seqLen; const detail::ScratchWorkspaces& scratch = this->template Input<detail::ScratchWorkspaces>(InputSize() - 1); const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Workspace>>& stepWorkspaces = scratch.stepWorkspaces; //... }Forward Pass Step Network
Create forward network and set input/output:
NetUtil forward(scope);
forward.SetType("rnn");
forward.AddInput("input_t");
forward.AddInput("timestep");
forward.AddInput(scope + "/hidden_t_prev");
forward.AddInput(scope + "/cell_t_prev");
forward.AddInput(scope + "/gates_t_w");
forward.AddInput(scope + "/gates_t_b");
Calculate R * C(t - 1) and add to W * X(t - 1)
auto fc = forward.AddFcOp(scope + "/hidden_t_prev", scope + "/gates_t_w",
scope + "/gates_t_b", scope + "/gates_t", 2);
auto sum = forward.AddSumOp({scope + "/gates_t", "input_t"}, scope + "/gates_t");
Add seq for recurrent calculation and add LSTMUnitOp
forward.AddInput(seq_lengths);
auto lstm = forward.AddLSTMUnitOp({scope + "/hidden_t_prev", scope + "/cell_t_prev", scope + "/gates_t", seq_lengths, "timestep"},
{scope + "/hidden_t", scope + "/cell_t"});
Add output of LSTM (Not Recurrent network).
forward.AddOutput(scope + "/hidden_t");
forward.AddOutput(scope + "/cell_t");
Backward Pass Step Network
Create backward network
NetUtil backward("RecurrentBackwardStep");
backward.SetType("simple");
backward.AddGradientOp(*lstm);
Replace output “LSTM/hidden_t_prev_grad” of FcGradient by “LSTM/hidden_t_prev_grad_split”, as the name “LSTM/hidden_t_prev_grad” conflicts with LSTMUnitGradient output.
auto grad = backward.AddGradientOp(*fc);
grad->set_output(2, scope + "/hidden_t_prev_grad_split");
Add the FcGradient part into δy(t - 1)
backward.AddSumOp(
{scope + "/hidden_t_prev_grad", scope + "/hidden_t_prev_grad_split"},
scope + "/hidden_t_prev_grad");
Define input of backward network
backward.AddInput(scope + "/gates_t");
backward.AddInput(scope + "/hidden_t_grad");
backward.AddInput(scope + "/cell_t_grad");
backward.AddInput("input_t");
backward.AddInput("timestep");
backward.AddInput(scope + "/hidden_t_prev");
backward.AddInput(scope + "/cell_t_prev");
backward.AddInput(scope + "/gates_t_w");
backward.AddInput(scope + "/gates_t_b");
backward.AddInput(seq_lengths);
backward.AddInput(scope + "/hidden_t");
backward.AddInput(scope + "/cell_t");
Recurrent Network
Create Recurrent network by RecurrentNetwork Operation
auto op = trainModel.AddOp("RecurrentNetwork",
{scope + "/i2h", hidden_init, cell_init, scope + "/gates_t_w",
scope + "/gates_t_b", seq_lengths},
{scope + "/hidden_t_all", hidden_output, scope + "/cell_t_all",
cell_state, scope + "/step_workspaces"}
);
What’s function of LSTM/step_workspaces?
Link Operation
Setup links for recurrent operation in time T
net_add_arg(*op, "link_internal",
std::vector<std::string>{
scope + "/hidden_t_prev",
scope + "/hidden_t",
scope + "/cell_t_prev",
scope + "/cell_t",
"input_t"});
net_add_arg(*op, "link_external",
std::vector<std::string>{
scope + "/" + scope + "/hidden_t_prev_states",
scope + "/" + scope + "/hidden_t_prev_states",
scope + "/" + scope + "/cell_t_prev_states",
scope + "/" + scope + "/cell_t_prev_states",
scope + "/i2h"});
net_add_arg(*op, "link_offset", std::vector<int>{0, 1, 0, 1, 0});
The link operation defined in recurrent_network_op.h as RNNApplyLinkOp and recurrent_network_op.cc AddApplyLinkOps
It maps part of external data into internal data as a pointer (reference).
const auto& t0 = this->template Input<Tensor>(0, CPU);
const auto t = t0.template data<int32_t>()[0];
auto& external = Input(1);
auto* internal_out = Output(0);
auto* external_out = Output(1);
CAFFE_ENFORCE_GT(external.numel(), 0);
const int64_t externalTimestepSize = external.numel() / external.size(0);
auto* externalData = external_out->template mutable_data<T>() +
(t + offset_) * externalTimestepSize;
auto internalDims = external_out->sizes().vec();
internalDims[0] = window_;
internal_out->Resize(internalDims);
internal_out->ShareExternalPointer(
externalData, externalTimestepSize * window_);
The link operation is like:
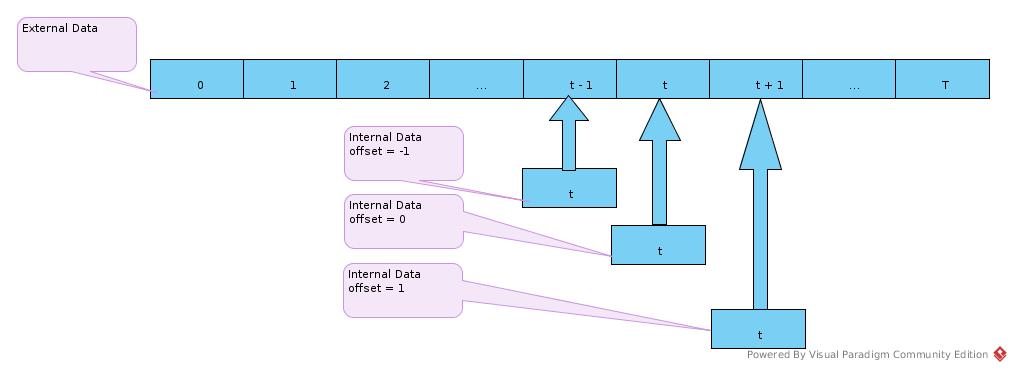
So, in above links, taking cell_t for example, at time t:
- the c(t) = LSTM/cell_t_prev points to LSTM/LSTM/cell_t_prev_states(t),
- the c(t + 1) = LSTM/cell_t points to LSTM/LSTM/cell_t_prev_states(t + 1),
the LSTM/LSTM/cell_t_prev_states(t + 1) would be filled in after RNN step t calculation, for calculation of step (t + 1)
Alias Operation
Then alias setup for forward network:
net_add_arg(
*op, "alias_src",
std::vector<std::string>{scope + "/" + scope + "/hidden_t_prev_states",
scope + "/" + scope + "/hidden_t_prev_states",
scope + "/" + scope + "/cell_t_prev_states",
scope + "/" + scope + "/cell_t_prev_states"});
net_add_arg(*op, "alias_dst",
std::vector<std::string>{
scope + "/hidden_t_all",
hidden_output,
scope + "/cell_t_all",
cell_state});
net_add_arg(*op, "alias_offset", std::vector<int>{1, -1, 1, -1});
Alias operation is similar to Link operation, to share part of source data into destination blob. The difference is that
- alias operation maps data of sequence of time steps.
- alias operation executed before recurrent operations.
const int32_t startDstTimestep = oc.offset >= 0 ? oc.offset : src->size(0) + oc.offset; const int32_t numDstTimesteps = src->size(0) - startDstTimestep;Other Arguments
- Timestep
The argument timestep is also an input of each recurrent operations.
It increase by 1 in forward pass and decrease by 1 in backward pass.
net_add_arg(*op, "timestep", "timestep"); - recompute_blobs_on_backward: Not defined
net_add_arg(*op, "recompute_blobs_on_backward");
void initializeBlobsToRecomputeOnBackward(Workspace* sharedBlobsWs) {
std::vector<std::string> v;
const auto& blobs = this->template GetRepeatedArgument<std::string>(
"recompute_blobs_on_backward", v);
for (const auto& b : blobs) {
// Note: if the blob already was created, this is a no-op.
sharedBlobsWs->CreateBlob(b);
}
}
- param, param_grads, outputs_with_grads,
param argument defines recurrent network parameters to be learned.
net_add_arg(*op, "param", std::vector<int>{3, 4});outputs_with_grads defines corresponding name in GradientOp as:
net_add_arg(*op, "param_grads", std::vector<std::string>{scope + "/gates_t_w_grad", scope + "/gates_t_b_grad"});The index(3, 4) follows sequence defined in forward network inputs as:
auto op = trainModel.AddOp("RecurrentNetwork", {scope + "/i2h", hidden_init, cell_init, scope + "/gates_t_w", scope + "/gates_t_b", seq_lengths}, {scope + "/hidden_t_all", hidden_output, scope + "/cell_t_all", cell_state, scope + "/step_workspaces"} );But in actual GradientOp parse, the indices are extracted in constuctParams as
for (int i = 0; i < param.size(); ++i) { detail::Param p; // Forward inputs come after [outputs_with_grads] gradient inputs p.param = operator_def.input(param[i] + gradInputs_.size()); // See GetRecurrentNetworkGradient to understand offseting here p.grad = operator_def.output(i + numSequences_); std::string grad_blob = param_grads.empty() ? p.grad : remappedName(param_grads[i]); p.cellGradient = grad_blob + "_tmpstep"; params.push_back(p); std::cout << "Construct params " << p.param << ", " << p.grad << ", " << p.cellGradient << std::endl; renameOpInputOutput(grad_blob, p.cellGradient); }The actual index is (param[i] + gradInputs_.size()), as the inputs/outputs of GradientOp are converted by GetRecurrentNetworkGradient::GetGradientDefs:
auto outputs_with_grads = argsHelper.GetRepeatedArgument<int32_t>("outputs_with_grads"); CAFFE_ENFORCE(outputs_with_grads.size() > 0); for (auto id : outputs_with_grads) { gradientInputs.push_back(GO(id)); } // All inputs and outputs are passed back for (int i = 0; i < def_.input_size(); ++i) { gradientInputs.push_back(I(i)); } for (int i = 0; i < def_.output_size(); ++i) { gradientInputs.push_back(O(i)); }As size of *outputs_with_grads” is 1:
net_add_arg(*op, "outputs_with_grads", std::vector<int>{0});The actual indices are 1 + 3 and 1 + 4, that matches inputs/outputs of GradientOp:
Generated gradient op input: "LSTM/hidden_t_all_grad" input: "LSTM/i2h" input: "hidden_init" input: "cell_init" input: "LSTM/gates_t_w" input: "LSTM/gates_t_b" input: "seq_lengths" input: "LSTM/hidden_t_all" input: "LSTM/hidden_t_last" input: "LSTM/cell_t_all" input: "LSTM/cell_t_last" input: "LSTM/step_workspaces" output: "LSTM/i2h_grad" output: "LSTM/gates_t_w_grad" output: "LSTM/gates_t_b_grad" output: "hidden_init_grad" output: "cell_init_grad"In constructParam, the param also has been renamed as:
p.cellGradient = grad_blob + "_tmpstep";As the ultimate gradient of these parameters are accumulation of gradients in each time step. So a temporary argument name created for each time step.
- recurrent_states, initial_recurrent_state_ids
In forward pass, recurrent_states is bound to initial_recurrent_state_ids.
The mapping is parsed in constructRecurrentInputs
std::vector<detail::RecurrentInput> constructRecurrentInputs( const OperatorDef& operator_def, Workspace* sharedWs) { //Seemed GetRepeatedArgument is to copy each element of input into created blob const auto states = this->template GetRepeatedArgument<std::string>("recurrent_states"); const auto inputs = this->template GetRepeatedArgument<int>("initial_recurrent_state_ids"); CAFFE_ENFORCE_EQ(states.size(), inputs.size(), "states/inputs mismatch"); std::vector<detail::RecurrentInput> ris; for (auto i = 0; i < states.size(); ++i) { // States need to be "global" (since they are shared between // forward and backward). sharedWs->CreateBlob(states[i]); detail::RecurrentInput ri; ri.state = states[i]; ri.input = operator_def.input(inputs[i]); ris.push_back(ri); } return ris; }The states initialization is defined in detail::initializeRecurrentInput. The annotation of function: ```c++ /**
- Copy external input to the step net into the first item of
- (T + 1) X batch_size X input_size tensor */ ```
In backward pass, recurrent_states is bound with alias_src and alias_offset. In constructRecurrentGradients, it finds the corresponding gradient of RNN network inputs. And the result is LSTM/LSTM/hidden_t_prev_states_grad ==> LSTM/hidden_t_all_grad
AddGradientInputAccumulationOps defines accumulation operation to get the gradient passed from upper layer in each time step. After gradients of all the time steps, the output is copied back into init blob for next forward pass:
for (int i = 0; i < recurrentInputIds_.size(); ++i) {
// See GetRecurrentNetworkGradient to understand offseting here
// Outputs of the gradient are inputs of the forward pass.
// So we need to offset on all inputs that go before recurrent
// initial ones
auto outputIdx = i + params_.size() + numSequences_;
// because first gradInputs_.size() inputs are from GO
int inputId = recurrentInputIds_[i] + gradInputs_.size();
VLOG(1) << "Resetting output " << this->debug_def().output(outputIdx)
<< " like input " << this->debug_def().input(inputId);
Output(outputIdx)->ResizeLike(Input(inputId));
T* output_data = Output(outputIdx)->template mutable_data<T>();
auto pBlob = sharedWs_->GetBlob(recurrentGradients_[i].grad);
CAFFE_ENFORCE(pBlob);
auto* p = BlobGetMutableTensor(pBlob, Context::GetDeviceType());
if (Input(inputId).dim() >= 2) {
// Gradient states blob should live. And if it gets changed by the
// backward pass, then output should be changed as well. Thus it should
// be okay to share data here
Output(outputIdx)->template ShareExternalPointer<T>(
p->template mutable_data<T>());
}
Step Network
Define forward network and backward network for each step execution
net_add_arg(*op, "step_net", forward.Proto());
net_add_arg(*op, "backward_step_net", backward.Proto());
In RecurrentNetworkOp::DoRunWithType:
for (auto t = 0; t < seqLen; ++t) {
auto& currentStepWorkspace =
(has_backward_pass ? stepWorkspaces[t] :
stepWorkspaces[t % num_workspaces_on_fwd_only]);
if (!currentStepWorkspace) {
currentStepWorkspace = std::make_shared<Workspace>(sharedBlobsWs.get());
}
if (rnnExecutor_) {
//...
} else {
// Use plain Caffe2 nets
detail::UpdateTimestepBlob(currentStepWorkspace.get(), timestep_, t);
auto* stepNet = currentStepWorkspace->GetNet(stepNetDef_.name());
if (stepNet == nullptr) {
stepNet = currentStepWorkspace->CreateNet(stepNetDef_);
}
CAFFE_ENFORCE(stepNet, "Step Net construction failure");
// Since we have a SimpleNet, there are no races here.
stepNet->RunAsync();
}
}
Similar in RecurrentNetworkGradientOp::DoRunWithType
Sequence
Forward Pass
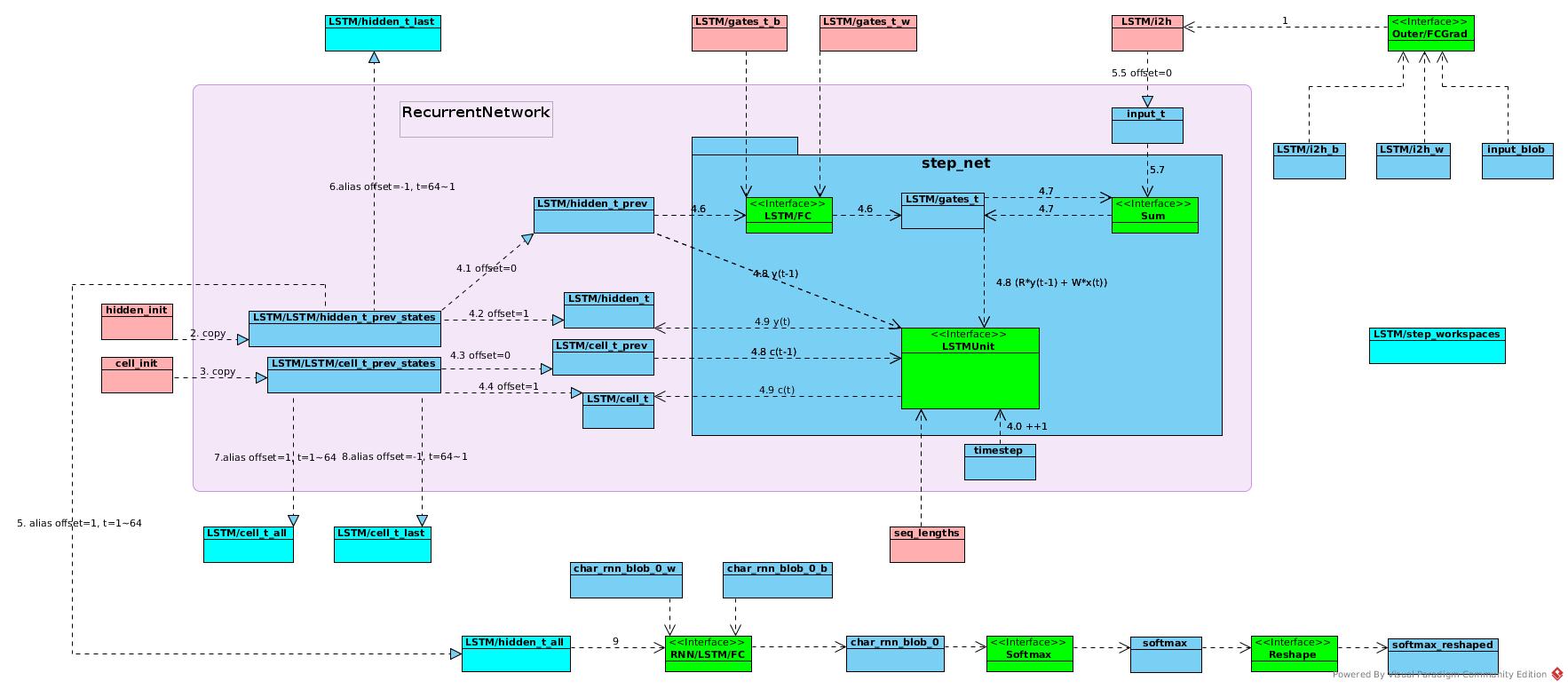
- Calculate (W * X) for all time steps
- Copy initiated value for hidden_t_prev_states time step 0
- Copy initiated value for cell_t_prev_states time step 0
- Recurrent network step at time t
- 4.0: update timestep value as t
- 4.1: LSTM/hidden_t_prev refers to LSTM/LSTM/hidden_t_prev_states values at t
- 4.2: LSTM/hidden_t refers to LSTM/LSTM/hidden_t_prev_states values at (t + 1) to restore LSTMUnitOp result
- 4.3: LSTM/cell_t_prev refers to LSTM/LSTM/cell_t_prev_states values at t
- 4.4: LSTM/cell_t refers to LSTM/LSTM/cell_t_prev_states values at (t + 1) to restore LSTMUnitOp result
- 4.5: input_t refers to LSTM/i2h values at t
- 4.6: (R * c(t - 1)) at time step t
- 4.7: (R * c(t - 1) + W * x(t)) at time step t
- 4.8: (R * c(t - 1) + W * x(t)), c(t - 1), y(t - 1) as inputs for all the gates and outputs
- 4.9: Get output of c(t) and y(t)
-
Map LSTM/LSTM/hidden_t_prev_states as LSTM/hidden_t_all. That y(t) for {t 0 <= t < sequenceLen} - Map LSTM/LSTM/hidden_t_prev_states as LSTM/hidden_t_last in reverse sequence for backward pass
- Map LSTM/LSTM/cell_t_prev_states as LSTM/cell_t_all, do not know further usage
- Map LSTM/LSTM/cell_t_prev_states as LSTM/cell_t_last for backward pass
- Calculate o(t) from y(t) for {t | 0 <= t < sequenceLen}, function is FC + Softmax
Backward Pass
Backward Propagation:
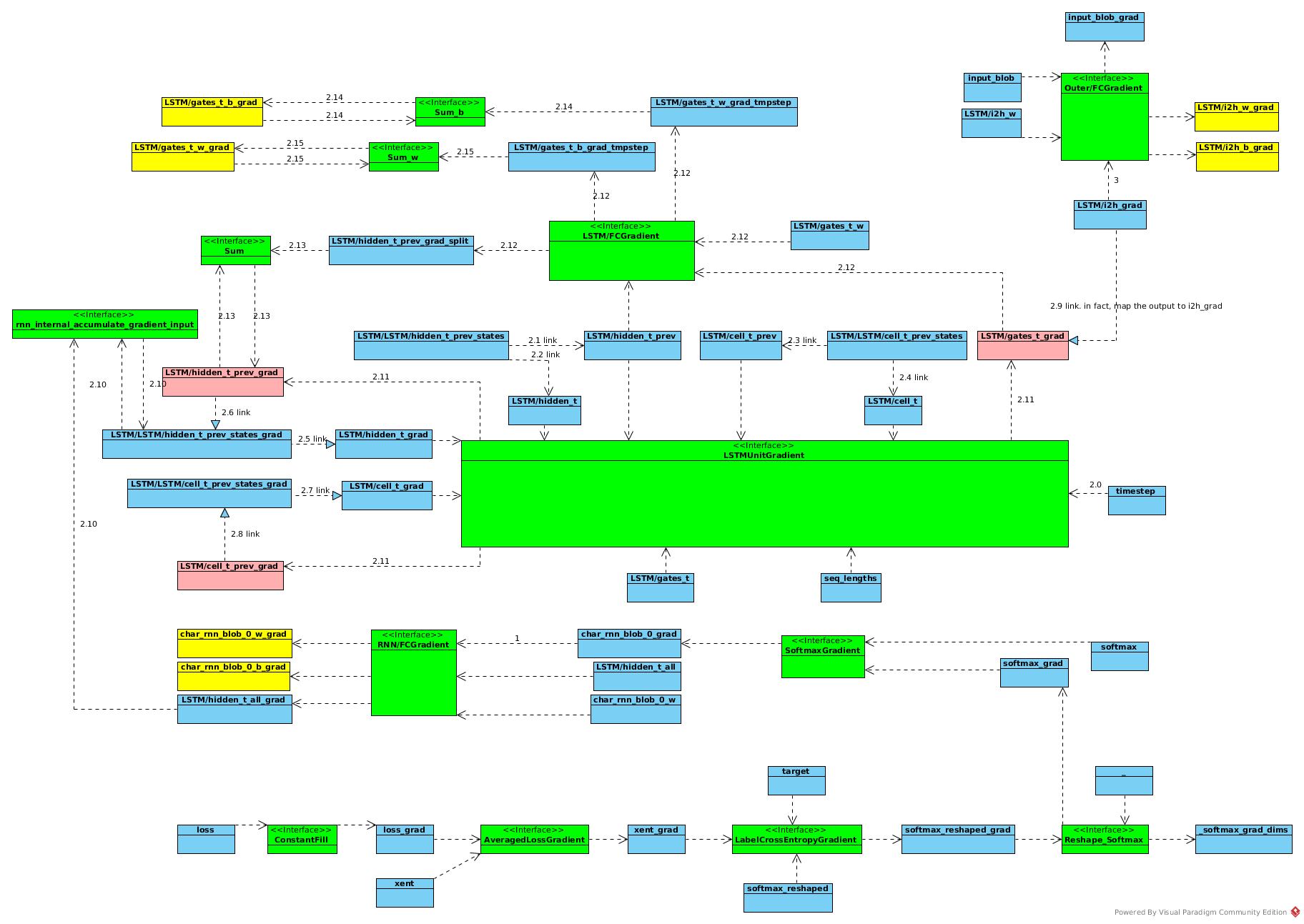 The output of SoftmaxGradient is accumulation of loss of all time steps.
The output of SoftmaxGradient is accumulation of loss of all time steps.
- Get δy of all the time steps
- Recurrent Gradient at time step t
- 2.0 update timestep value as t
- 2.1 Get y(t)
- 2.2 Get y(t + 1)
- 2.3 Get c(t)
- 2.4 Get c(t + 1)
- 2.5 Get δy(t + 1)
- 2.6 Get address of δy(t)
- 2.7 Get δc(t + 1)
- 2.8 Get address of δc(t)
- 2.9 Get address of δz(t)
- 2.10 Get and add part of δy(t + 1) from upper layer
- 2.11 LSTMUnitGradient outputs δy(t), δc(t), δz(t)
- 2.12 Get part of δy(t) from δ(R * y)/δy
- 2.13 Add it into original δy(t) and map it into LSTM/LSTM/hidden_t_prev_states_grad for (t - 1)
- 2.14 Get δR in step t and have it accumulated
- 2.15 Get δRb in step t and have it accumulated
- When all δz(t) calculated, get the δW and δWb
Update